This post is about how to use android debug bridge (adb) to debug or access android device. The adb is a toolkit included in the Android SDK package. It consists of both client and server-side programs that communicate with one another. The adb is typically accessed through the command-line interface. The adb is also a versatile tool that lets you communicate with an emulator instance or connected Android-powered device.
Basic functions we can perform using the adb are:
- adb push/pull (to copy data from or to android device)
- adb backup/restore (to take backup or restore)
- adb logcat (show live log of all processes running on device)
- adb shell (used for package manager, activity manager)
To use this you need Android SDK package that can be downloaded from Here. You can find the
adb tool in <sdk>/platform-tools/. Go to folder in which adb package is available and enter command "chmod +x adb"NOTE: if you are using Linux then type './' before every command(if PATH is not set).
Connected using USB cable:
"adb kill-server"
"adb start-server"
"adb devices"
You will find serial number of device as connected by given commands. Now you are ready to perform following task.
ADB functions:
1) adb push/pull
- Copy file from computer to device:
"adb push README.rst /mnt/sdcard"
- Copy file from device to computer:
"adb pull /mnt/sdcard/README.rst /tmp"
- Copy folder from computer to device
- Copy folder from device to computer
2) adb backup/restore
- Take backup:
"adb backup -all -f /tmp/backup.ab"
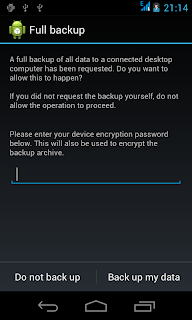
Now unlock your android device, and select "Backup up my data". You can optionally set a
password too. This process doesn't has progress bar.
password too. This process doesn't has progress bar.
- Restore from previous backup:
"adb restore /tmp/backup.ab"
This will again ask for confirmation on android side, select "Restore my data" to start restore
process. This process also doesn't has progress bar.
3) adb logcat:
3) adb logcat:
- This will simply show live log of all processes running on device.
"adb logcat -d"
4) adb shell:
- This is to execute any shell command inside android environment. General syntax is
"adb shell <command>"
- package manager (pm)
(pm) tool perform actions and queries on application packages installed on the device. Syntax to
use
use
"adb shell pm <command>"
To retrieve package list of installed application
"adb shell pm list packages"
To uninstall package
"adb shell pm uninstall com.example.my_app"
To set install location for apk's, internal or external sdcard
"adb shell pm set-install-location <code>"
0 : Auto—Let system decide the best location
1 : internal device storage
2 : external media
To get current install location
"adb shell pm get-install-location"
- activity manager (am)
Within an adb shell, one can issue commands with the activity manager (am) tool to perform
various system actions, such as start an activity, force-stop a process etc.
various system actions, such as start an activity, force-stop a process etc.
"adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW"
This will open "Complete action using" menu.
kill all background apps
"adb shell am kill-all"
Hope this information will help you.
I would really appreciate your feedback, suggestions, requests and ideas.
Thank You.
Thank You.
Thanks for sharing this. I am not too good with these things so I have been researching online for a good performance monitoring software to monitor everything for my small business. I have to find what's easiest for me
ReplyDeleteExcellent information with unique content and it is very useful to know about the information based on blogs.
ReplyDeletebest graphic design courses in hyderabad
Wow, incredible blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is excellent, let alone the content! web agency berlin
ReplyDelete